Spinal Disc Herniation: Causes and Care
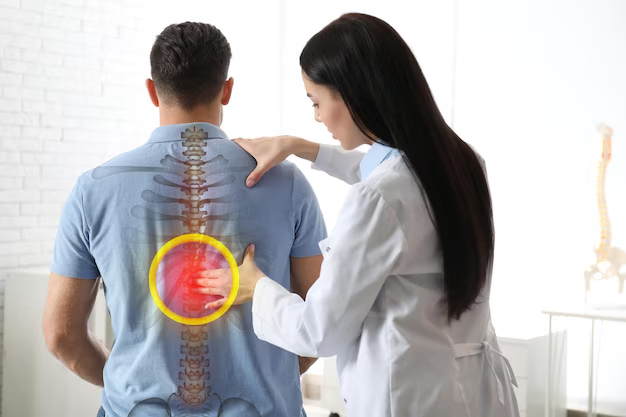
Spinal disc herniation, commonly known as a slipped or ruptured disc, occurs when the soft inner gel of an intervertebral disc pushes through its outer layer. This can lead to nerve compression, causing pain, numbness, and weakness.
Causes & Risk Factors
-
Age-Related Degeneration – Discs lose flexibility and become prone to rupture over time.
-
Injury or Trauma – Sudden impact or strain can cause a disc to herniate.
-
Repetitive Movements – Frequent bending, lifting, or twisting increases stress on the spine.
-
Obesity – Excess weight adds pressure to the spinal discs.
-
Genetics – Family history may increase susceptibility to disc problems.
-
Sedentary Lifestyle – Weak back muscles contribute to poor spinal support.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary based on the location of the herniation:
-
Lower Back (Lumbar Herniation) – Sciatic pain radiating down the leg, tingling, numbness, and difficulty walking.
-
Neck (Cervical Herniation) – Shoulder and arm pain, weakness, and loss of sensation in the hands.
-
Thoracic Region (Rare) – Mid-back pain and nerve-related symptoms affecting the chest or abdomen.
Diagnosis
-
Physical Examination – Evaluates mobility, reflexes, and strength.
-
MRI & CT Scans – Provide detailed imaging of disc damage and nerve compression.
-
X-rays – Rule out other spinal conditions.
-
Electromyography (EMG) – Assesses nerve function and identifies nerve compression.
Treatment Options
-
Rest & Activity Modification – Avoiding strenuous activities allows healing.
-
Medications – Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants help manage symptoms.
-
Physical Therapy – Strengthening and stretching exercises improve spinal stability.
-
Epidural Steroid Injections – Reduce inflammation around the affected nerve.
-
Surgery (Last Resort) – Procedures like microdiscectomy or spinal fusion may be necessary for severe cases.
Prevention & Lifestyle Tips
-
Maintain Good Posture – Proper spinal alignment reduces strain.
-
Exercise Regularly – Strengthening core and back muscles supports the spine.
-
Lift Properly – Use legs instead of the back when lifting heavy objects.
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight – Reduces stress on spinal discs.
-
Avoid Prolonged Sitting – Take breaks and stretch frequently.
Conclusion
Spinal disc herniation can cause significant discomfort but is manageable with proper care. Early intervention, lifestyle adjustments, and medical guidance can help prevent long-term complications. If you experience persistent back pain or nerve-related symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and treatment.
More Posts
ㅤ

